As numerous tech companies race to enhance the multimodal capabilities of large models and strive to integrate functions like text summarization and image editing into mobile devices, OpenAI has launched a new product! CEO Samuel Harris Altman expressed his state with three letters: her (just like the movie “Her”).

In the early morning of May 14th, at OpenAI Spring Update the latest GPT-4o was officially unveiled, showcasing a series of new features. This not only revolutionized the product’s form but also once again stirred the global tech community. As an advanced large model for human-computer interaction, GPT-4o integrates the understanding of text, speech, and images. Its rapid response speed, rich emotional expression, and profound understanding of human behavior mark yet another leap forward in the field of human-computer interaction.
Watch the video of the OpenAI Spring Update
Everyone marvels at the arrival of the era of “Movie-Her,” and AI’s Ultra-Humanlike is also gaining significant attention. Personified TTS (Text-to-Speech) refers to systems that can simulate features of natural conversation, such as extended sounds, pauses, colloquial vocabulary fillers, repetition, inversion, and emphasis. To achieve this, TTS models must replicate these conversational features during modeling and consider both textual and acoustic contexts.
Moreover, the model needs to pay attention to more non-verbal information to enhance the naturalness and expressiveness of the speech. Below is an evaluation of various indicators for a Base TTS model, showing that the scores for prosody and emotion are the lowest. This indicates that emotion and prosody synthesis remain the most challenging tasks in speech synthesis.
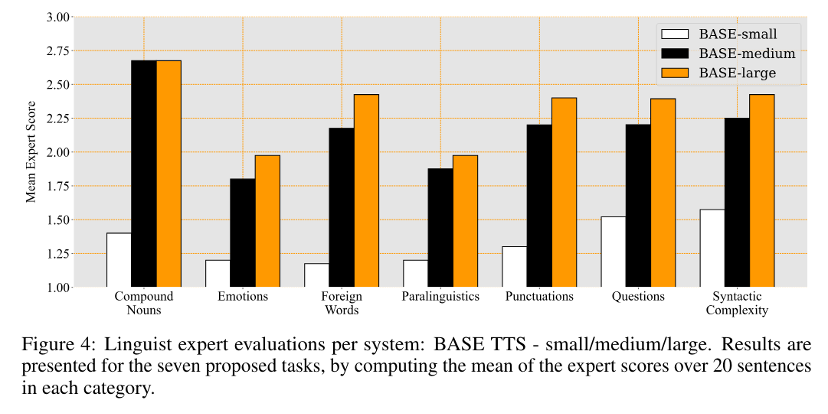 From BASE TTS: Lessons from building a billion-parameter Text-to-Speech model on 100K hours of data
From BASE TTS: Lessons from building a billion-parameter Text-to-Speech model on 100K hours of data
The challenges of developing anthropomorphic TTS systems
1.Data Acquisition and Processing
One of the major challenges in developing personified TTS (Text-to-Speech) systems is data acquisition and processing.
Firstly, to train a TTS system capable of accurately handling non-verbal information such as intonation, intensity, and emotional states, a large amount of high-quality, meticulously labeled speech data is required. This data labeling should not only include textual information but also detailed records of various acoustic features of the speech, so the system can learn and reproduce the complex variations found in natural speech.
Secondly, the diversity of speech data is a key factor. Since people from different regions, genders, and age groups exhibit unique speech characteristics and habits, it is essential to collect speech samples from a wide range of backgrounds to ensure that the TTS system performs well across various accents and language styles. This includes various dialects, accents, and a range of language styles from formal to informal, to ensure the system’s broad applicability and naturalness. Therefore, high-quality and diverse data collection and processing become one of the significant challenges in developing personified TTS systems.

2.Model Design and Training
The development of anthropomorphic TTS (Text-to-Speech) systems faces significant challenges in terms of model design and training, primarily focusing on two major areas: model complexity and the naturalness and consistency of the voice.
(1) Model Complexity
To accurately capture and reproduce human paralinguistic information such as intonation, pauses, emphasis, and emotional changes, TTS models must possess a high degree of complexity and expressiveness. This requires the model not only to understand the literal meaning of the text but also to deeply analyze the emotions and context contained in the text, and then reflect these subtle differences in the voice output.
Automatic detection of emotions is achieved through NLP (Natural Language Processing) techniques, such as sentiment analysis, but how to map these emotions to specific vocal expressions, such as the pitch of the voice, the speed of speech, and the volume, remains a cutting-edge issue in AI research.
In addition, the model also needs to be able to handle various complex speech patterns and non-standard language expressions, such as dialects, accents, or the speaking habits of specific groups.
(2) Naturalness and Consistency of the Voice
In natural conversation, people constantly adjust their intonation and speech rate according to the context and emotional state, which is extremely difficult to achieve in TTS systems.
Although modern TTS systems have been able to improve the naturalness of voice synthesis by adopting advanced machine learning models such as deep neural networks, there are still challenges in maintaining the consistency and authenticity of voice output. Especially when dealing with long texts or complex conversations, maintaining the fluency and naturalness of the voice while not losing the true expression of emotions is a technical difficulty.
Furthermore, to enhance naturalness, TTS systems often need to make complex decisions in real-time to adapt to changes in text content, which puts higher demands on the efficiency and response speed of real-time voice generation algorithms.
In response to these challenges, researchers are exploring directions including but not limited to: enhanced emotional modeling techniques, context-aware speech generation algorithms, and methods of deep learning training using large-scale data. By conducting in-depth analysis and learning of a large amount of voice data, TTS systems can better understand and simulate the diversity and complexity of human language, thereby improving the naturalness and application range of voice synthesis.
3.Solutions to Address Challenges
(1) TTS with the Aid of Large Language Models (LLMs)
Zhifan Guo et al. have developed a Text-to-Speech (TTS) system (referred to as PromptTTS), which takes prompts containing descriptions of style and content as input to synthesize corresponding speech.
PromptTTS comprises a style encoder and a content encoder, which extract the respective representations from the prompts, as well as a speech decoder that synthesizes speech based on the extracted style and content representations. Compared to previous controllable TTS works that require users to have acoustic knowledge to understand stylistic factors such as prosody and pitch, PromptTTS is more user-friendly because text descriptions are a more natural way to express speech style. The model is adept at capturing paralinguistic information such as style and prosody in speech synthesis.
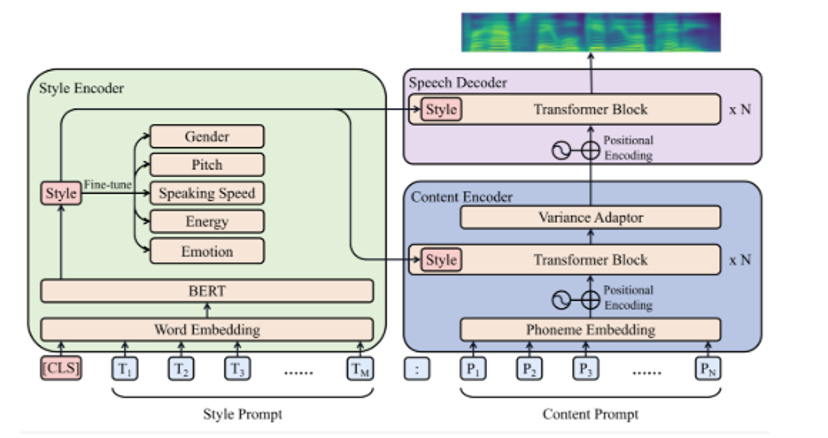 From PROMPT TTS: controllable Text-to-Speech with text descriptions
From PROMPT TTS: controllable Text-to-Speech with text descriptions
(2) Synthetic Database with Paralinguistic Annotations
Due to the scarcity of TTS databases with fine-grained annotations containing paralinguistic tags, there is currently little research that enhances the synthesis of paralinguistic features in TTS systems through direct training rather than relying on language models.
However, training TTS models directly with these data can more directly and effectively learn how to express emotions, tone, and other paralinguistic features, simplify the system architecture, improve the consistency and quality of data, enhance the model’s generalization ability, and reduce dependence on external systems. This provides developers with better customization options, allowing for the optimization of TTS output for specific needs.
Despite the significant benefits of direct training, the challenges are substantial, especially in terms of the considerable time and resource investment required to obtain high-quality annotated data, and may also require the development of new technologies to maximize the utility of the data.
Dataocean AI’s Fine-Grained Paralanguage Dataset
To address the shortage of Chinese speech synthesis databases with fine-grained annotations of paralinguistic information currently available on the market, Dataocean AI has launched an innovative fine-grained paralinguistic dataset, which has been meticulously annotated for paralinguistic phenomena such as vocal drag, emphasis, and pauses.
The focus is mainly on casual speech materials in dialogue environments, which are highly suitable for training and optimizing Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems to enhance their naturalness and expressiveness in practical conversational applications. The features of this database include:
– Rich Paralinguistic Annotations
Each piece of speech data is not only annotated with basic pronunciation and intonation information but also finely marked with various paralinguistic information such as vocal drag, emphasis, and pauses, enabling TTS systems to more realistically reproduce human language expression.
– Conversational Corpus Design
All materials are based on dialogue scenarios, especially casual conversations, which help TTS systems to be better applied to interactive applications such as chatbots and virtual assistants.
– High-Quality Audio Collection
Recorded using professional recording equipment in acoustically treated environments to ensure the purity and high quality of the voice data.
The newly launched fine-grained paralinguistic information Chinese speech synthesis dataset will become a powerful tool for developers in fields such as AI chatbots, virtual assistants, educational software, and entertainment games, greatly enhancing the naturalness and expressiveness of voice interaction.
King-TTS-121 Chinese Multi-speaker Speech Synthesis Corpus (Multiple Styles Virtual Lovers)
King-TTS- 157 Chinese Mandarin Female Speech Synthesis Corpus (Interview of Customer Service Style)